
Measurement & Scaling in research / business (Research)
Measurement & Scaling in research / business research.
GET INSTANT HELP FROM EXPERTS!
- Looking for any kind of help on your academic work (essay, assignment, project)?
- Want us to review, proofread or tidy up your work?
- Want a helping hand so that you can focus on the more important tasks?
Hire us as project guide/assistant. Contact us for more information
Measurement & Scaling: Introduction
Measurement
Assigning numbers or other symbols to characteristics of objects according to certain specified rules.
- Numbers permit statistical analysis of data
- Numbers facilitate the communication of measurement of rules and results
Specification of rules for assigning numbers to the characteristics is especially important
Assignment process must be isomorphic , one to one correspondence between the number and characteristics being measured
Rules should be standardized and applied uniformly
Scaling
Scaling is the generation of a continuum upon which measured objects are located.
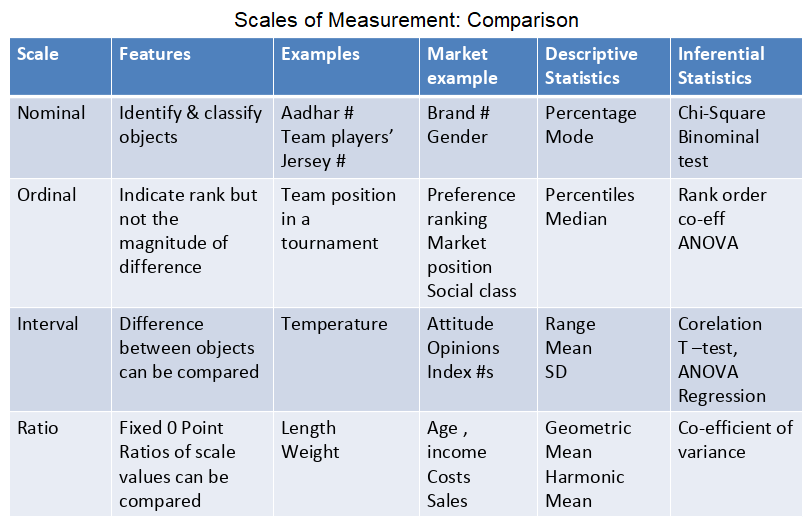
Scales of Measurement are: Nominal, Ordinal, Interval, Ratio
Scales of Measurement
Nominal Scale
- Figurative labeling
- Numbers serve as labels/ tags
- Aadhar numbers/ T-shirt numbers of players
Used for identifying respondents, brands, attributes, stores and other objects.
When used for classification purposes, the nominal scaled numbers serve as labels for categories / class
Operation : Counting
Statistics : based on frequency counts
Ordinal Scale
It is a Ranking Scale.
Possible to determine whether an object has more or less of a characteristic than some other objects
Indicates relative position and not the magnitude of difference between the objects
Used to measure relative attitudes, opinions, preferences and perceptions
Counting Operations & operations based on Centiles
Interval Scale
In an interval scale, numerically equal distances on the scale present equal values on the characteristics being measured.
Interval scales contains all the information of an ordinal scale but it also allows to compare the differences between objects.
Ratio Scale
All properties of Nominal, Ordinal & Interval scale plus an absolute zero point.
Identify, classify objects , compare intervals and differences.
Can be subjected to all statistical manipulations.
Comparative & Non-Comparative Scale
Scales can be:
Comparative
It involves the direct comparison of stimulus objects. The data must be interpreted in relative terms and have only ordinal properties.
Example: Paired Comparison, Rank Order, Q-Sort, Constant Sum
Non-Comparative
Each object is scaled independently of the others in the stimulus set. The data is assumed to be interval or ratio scaled.
Examples: Continuous, Itemized Rating Scales, Likert, Semantic Difference, Stapel
Advantages of Comparative Scales
- Small differences can be deducted between stimulus objects
- Same reference points for all respondents
- Easily understood
- Involves fewer theoretical assumptions
- Reduces the halo or carryover effects
Relative Disadvantages of Comparative Scales
- Ordinal Data
- Inability to generalize beyond the stimulus objects scaled
Comparative Scale
Paired Comparison Scaling
A respondent is presented with 2 objects and asked to select one according to some criterion. Data obtained is ordinal. Most widely used comparative technique. For n brands, [ n(n-1)/2] paired comparisons are requiredRank Order Rating
Respondents are asked to arrange a number of objects as per some criterion – taste/ looks/ quality etc.
The result is an ordinal scale which tells you which the most preferred to the least preferred but nothing about the distance between any of the objects.
Most realistic in representing the actual shopping situation.
Rank Order Scaling:
Please rank the following teas on the basis of its refreshing ability ( place 1 besides the rank you think is the most refreshing and 5 for the least refreshing)
Brooke Bond Red Label ( 3)
Tata Tetley ( 2)
Lipton Green Tea(1)
Taj Mahal Classc ( 4)
Wagh Bakri CTC ( 5)
Constant Sum
Respondents are to allocate a given number of points among the given objects according to some criterion.
Respondents are advised to allocate their points in proportion to their preference for the object.
Please divide the following 100 points among the following cars on the basis of fuel efficiency.
Maruti Alto – 50
Chevorlet Spark -20
Honda Brio – 30
Non-Comparative Scale
- Continuous Scale
- Interval Scale: Itemized Rating Scale, Semantic Differential Scale, Stapel Scale
Continuous Rating Scale
Graphic Rating Scale
Scale runs from one extreme of the criterion variable to another extreme
Respondents mark an appropriate position on the scale
Itemized Rating Scale
Likert Scale
Measurement scale with 5 response categories ranging from strongly disagree to strongly agree.
The respondent is to indicate a degree of agreement /disagreement with each of a series of statement.
Example of Likert Scale:
Statements: SD = 1, Disagree =2, Neither A nor D = 3, Agree = 4, S A =5
Flipkart offers a good mix of brands (Enter the choice)
Flipkart offers reasonable prices (Enter the choice)
Flipkart customer service is good (Enter the choice)
Semantic Differential Scale
7 point rating, Endpoints have bipolar labels.
For example:
Tata automobiles are:
Reliable _ X_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ Unreliable
Modern _ _ _ _ _X _ _ _ _ Old – Fashioned
Staple
Measures attitude that consist of single adjective in middle of an even numbered range of values from -5 to + 5 without a neutral point.
Commonly used Scales
Importance
Very Important, Important, Neither Important nor Unimportant, Unimportant, Very Unimportant
Satisfaction
Very Satisfied, Satisfied, Neither Satisfied nor Unsatisfied, Unsatisfied , Very Unsatisfied
Likely
Highly Likely, Likely ,Unlikely, Highly Unlikely
Scale Evaluation
- Error
- Reliability: Test/ Retest
- Validity
- Generalizability
Measurement Error
Variation on the information sought by researchers and the information generated by the measurement process employed.
Two types of Errors: Systematic Errors, Random Error.
Reliability
Consistent Results on repeated measurement
Impact of Systematic error on Reliability
Impact of Random error on Reliability
Validity
Extent to which difference in observed scale scores reflect true differences among objects on the characteristic being measured rather than Systematic Error or Random Error. (Perfect Validity would then be ?).
Relationship between Reliability and Validity:
Perfectly Valid = Perfectly Reliable
Reliable “is not equal to” Perfectly Valid

Leave a Reply